You can use the Literal platform to instrument OpenAI API calls. This allows you to track and monitor the usage of the OpenAI API in your application and replay them in the Prompt Playground.
The OpenAI instrumentation supports sync, async, streamed and regular responses!
Instrumenting OpenAI API calls
import os
from literalai import LiteralClient
"""
You need to call the `instrument_openai` method from the Literal client to
enable the integration. Call it before any OpenAI API call.
"""
literal_client = LiteralClient(api_key=os.getenv("LITERAL_API_KEY"))
literal_client.instrument_openai()
# Now you can use the OpenAI API as you normally would
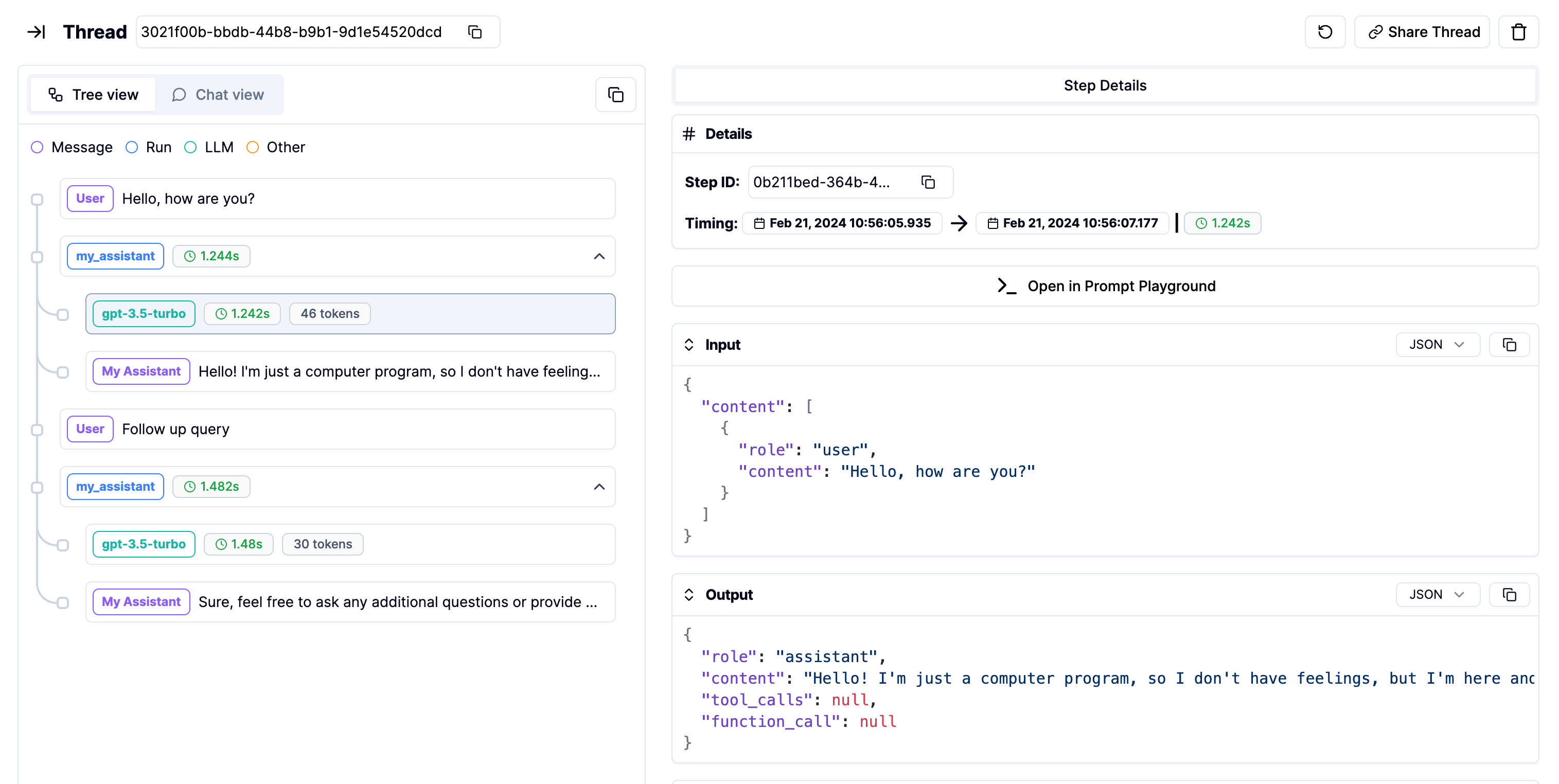
With Threads and Steps
You can use Threads and Steps on top of the OpenAI API to create structured and organized logs.
import os
from literalai import LiteralClient
from openai import OpenAI
openai_client = OpenAI()
literal_client = LiteralClient(api_key=os.getenv("LITERAL_API_KEY"))
literal_client.instrument_openai()
@literal_client.step(type="run")
def my_assistant(user_query: str):
completion = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": user_query,
}
],
)
literal_client.message(content=completion.choices[0].message.content, type="assistant_message", name="My Assistant")
def main():
with literal_client.thread(name="Example") as thread:
initial_user_query = "Hello, how are you?"
literal_client.message(content=initial_user_query, type="user_message", name="User")
my_assistant(initial_user_query)
follow_up_query = "Follow up query"
literal_client.message(content=follow_up_query, type="user_message", name="User")
my_assistant(follow_up_query)
main()
# Network requests by the SDK are performed asynchronously.
# Invoke flush_and_stop() to guarantee the completion of all requests prior to the process termination.
# WARNING: If you run a continuous server, you should not use this method.
literal_client.flush_and_stop()
Threads page: