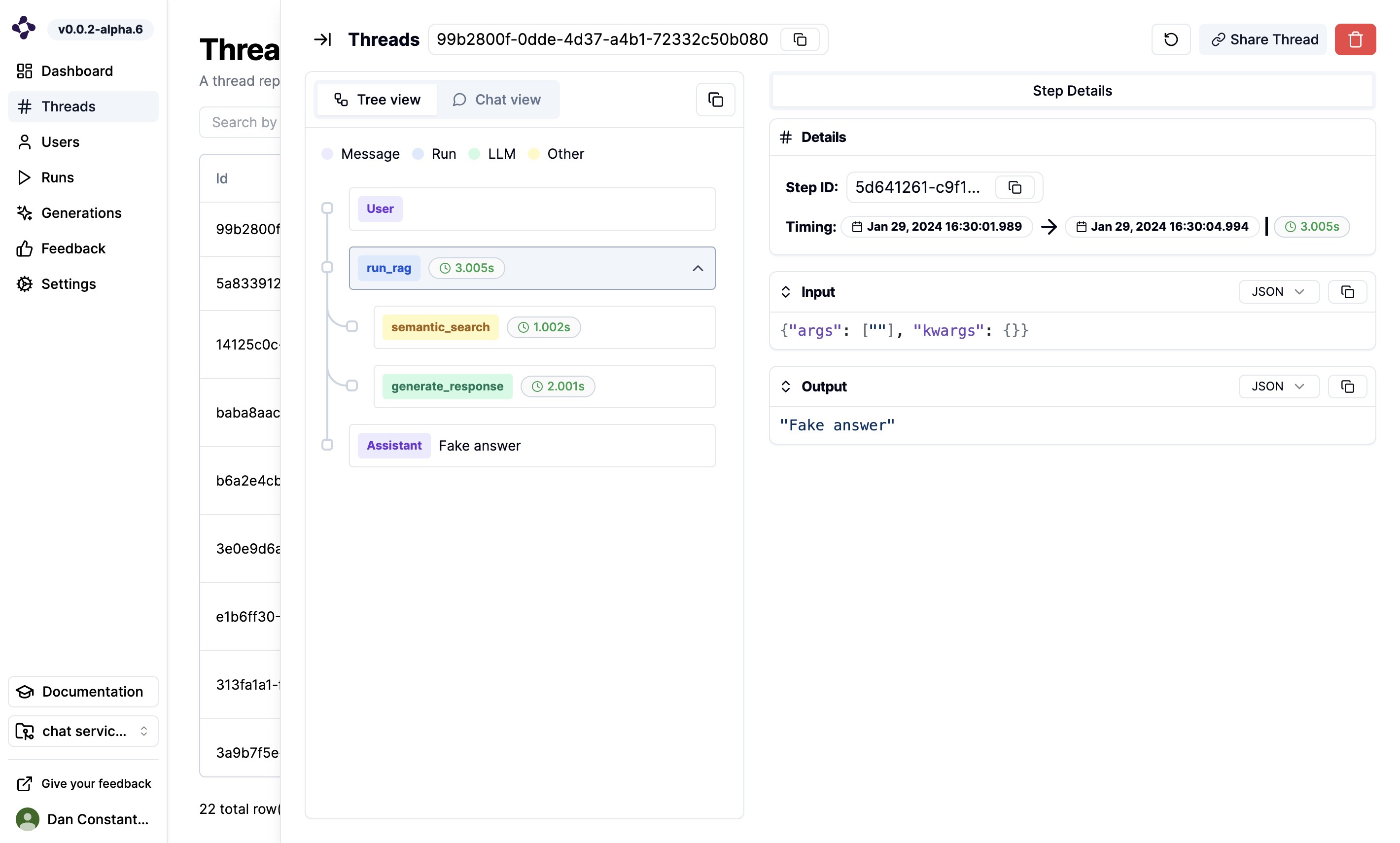
import asyncio
import os
from literalai import LiteralClient
client = LiteralClient(api_key=os.getenv("LITERAL_API_KEY"))
@client.step(type="retrieval")
async def semantic_search(question: str):
await asyncio.sleep(1)
return ["chunk 1", "chunk 2", "chunk 3"]
@client.step(type="llm")
async def generate_response(question: str, search_results: list):
await asyncio.sleep(2)
return "Fake answer"
@client.step(type="run")
async def run_rag(question: str):
results = await semantic_search(question)
answer = await generate_response(question, results)
return answer
@client.thread
async def main():
question = input("What is your question?")
client.message(content=question, type="user_message", name="User")
answer = await run_rag(question)
client.message(content=answer, type="assistant_message", name="Assistant")
print(answer)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
# Network requests by the SDK are performed asynchronously.
# Invoke flush_and_stop() to guarantee the completion of all requests prior to the process termination.
# WARNING: If you run a continuous server, you should not use this method.
client.flush_and_stop()